Introduction
The field of neurorehabilitation has made significant strides over the past few decades, largely driven by technological advancements that have revolutionized how patients with neurological disorders are treated. Among these innovations, bionic robots have emerged as one of the most promising tools in enhancing the effectiveness of neurorehabilitation. By mimicking the functions and capabilities of the human body, these robots offer unprecedented potential in restoring motor functions, improving neural recovery, and enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals suffering from conditions like stroke, spinal cord injuries, and other neurological impairments.
Bionic robots in neurorehabilitation are designed to integrate seamlessly with the human nervous system, allowing for real-time feedback and interaction with the brain’s neuroplasticity—the process by which the brain reorganizes itself and forms new neural connections. This interaction between robotics and neural systems holds the key to improving rehabilitation outcomes, offering a form of therapy that is personalized, effective, and scalable.
In this article, we will explore the role of bionic robots in the field of neurorehabilitation, detailing how they function, the technological innovations behind them, their current applications, and the challenges and future directions for their development. The goal is to understand not only the science and engineering behind these devices but also their immense potential in reshaping rehabilitation therapies and transforming the lives of individuals with neurological disorders.
What Are Bionic Robots?
Bionic robots, also referred to as biomechanical robots or neuroprosthetics, are devices designed to replicate the functionality of the human body. These robots can assist, augment, or even restore motor functions that are impaired due to neurological injuries or diseases. Unlike traditional rehabilitation methods, which rely heavily on manual therapy or passive equipment, bionic robots provide active, assistive interaction that adapts to the patient’s needs and progress.
At the core of bionic robots is their ability to interface with the nervous system. This interaction is achieved through a combination of sensors, actuators, and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, which allow the robot to interpret neural signals, adjust its actions based on feedback from the user, and provide real-time assistance.
Components of Bionic Robots:
- Sensors: These are used to detect the user’s movements or intentions. They may include electromyography (EMG) sensors, which measure electrical activity in muscles, or brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), which detect neural signals directly from the brain.
- Actuators: These are mechanical components that carry out the movements and provide feedback to the user. Actuators can simulate the range of motion of human joints or assist in the movement of paralyzed limbs.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms help bionic robots adapt to the patient’s condition over time, learn from the user’s movements, and provide tailored rehabilitation exercises. AI is also used in processing complex data from sensors to guide and adjust the robot’s movements.
- Neuroplasticity Integration: By facilitating controlled, repetitive motion and providing real-time feedback, bionic robots stimulate the brain’s natural ability to form new neural connections, a process known as neuroplasticity.
The Role of Bionic Robots in Neurorehabilitation
1. Restoring Motor Function through Neuroplasticity
The fundamental goal of neurorehabilitation is to promote recovery of motor functions in patients with neurological impairments. After a stroke, spinal cord injury, or neurodegenerative disease, the brain’s motor pathways may become damaged or dysfunctional, leading to partial or complete loss of movement. The rehabilitation process focuses on retraining the brain to regain control over these impaired functions.
Bionic robots are particularly effective in promoting neuroplasticity. By providing patients with controlled, repetitive movements, these robots encourage the brain to form new neural pathways, which can compensate for lost or damaged functions. The precise and consistent assistance offered by bionic robots enables patients to perform movements they would otherwise be unable to do on their own, thereby speeding up the recovery process.
- Rehabilitation After Stroke: Stroke patients often suffer from paralysis or weakness on one side of the body due to damage to the brain’s motor cortex. Bionic robots, such as exoskeletons or robotic arms, help stroke patients regain strength and coordination by providing targeted assistance. The robots guide the patient’s movements while also providing sensory feedback that encourages the brain to “rewire” itself and recover motor function.
- Spinal Cord Injury Recovery: For individuals with spinal cord injuries, bionic robots can offer mobility assistance through robotic exoskeletons. These wearable devices enable patients with lower limb paralysis to stand, walk, and even climb stairs, promoting neural recovery and improving cardiovascular health.
- Motor Learning and Training: Bionic robots can also be used for motor learning, which is a process that involves practicing and refining motor skills. With regular use, patients can improve their motor abilities and achieve functional independence. The robots provide consistent practice and feedback, helping patients overcome challenges like muscle weakness, spasticity, or coordination deficits.
2. Enhancing Therapy with Real-Time Feedback
A key feature of bionic robots in neurorehabilitation is their ability to provide real-time feedback. Unlike traditional therapies, which often lack interactivity, bionic robots can adjust their movements based on the patient’s input, adapting the level of assistance provided to match the patient’s needs at each stage of recovery.
- Active Assistance: For example, in the case of robotic exoskeletons, the device can provide both active assistance and passive movement depending on the patient’s abilities. As the patient gains strength and control over their movements, the robot reduces its level of assistance, encouraging the patient to take over more of the movement independently.
- Biofeedback: Many bionic rehabilitation robots use biofeedback mechanisms, such as EMG feedback, to provide immediate sensory cues to the patient. This feedback helps patients better understand how their muscles are functioning, improving motor control and facilitating the development of more efficient movement patterns.
- Adjustable Difficulty Levels: The robot can modify the difficulty level of exercises based on real-time performance metrics. This ensures that the rehabilitation process is challenging yet achievable, pushing the patient to improve without overexerting themselves.
3. Personalization of Rehabilitation
Bionic robots enable personalized rehabilitation programs that can be tailored to the specific needs and progress of each patient. Through continuous monitoring and data collection, the robots can adjust the therapy based on individual goals, movement patterns, and physical condition.
- Adaptive Learning: Machine learning algorithms integrated into the robots allow them to adapt to the unique rehabilitation needs of each patient. The robot learns from the patient’s performance and adjusts therapy parameters accordingly. This customization ensures that the patient receives the most effective treatment possible.
- Long-Term Monitoring and Assessment: Bionic robots can track progress over time, providing valuable data for clinicians to assess recovery. This allows for more precise treatment adjustments and enables clinicians to measure outcomes in a data-driven manner.
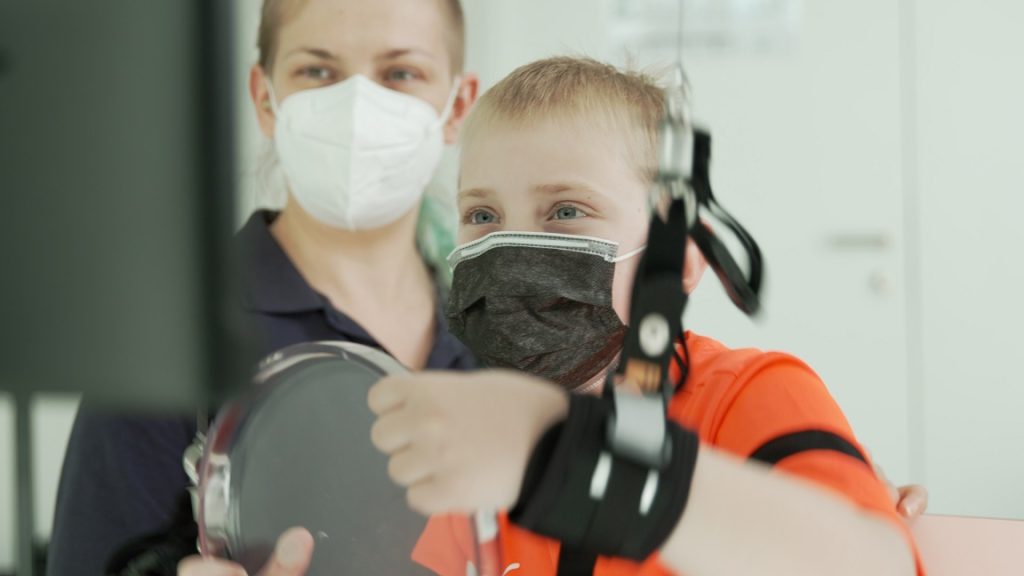

Current Applications of Bionic Robots in Neurorehabilitation
1. Robotic Exoskeletons
Robotic exoskeletons are wearable devices that assist individuals with mobility impairments, allowing them to stand, walk, and perform other activities. These exoskeletons are a breakthrough in neurorehabilitation for patients with spinal cord injuries and stroke, providing physical support and promoting the re-engagement of neural circuits involved in walking.
- ReWalk: One of the most well-known robotic exoskeletons, ReWalk, helps individuals with lower limb paralysis regain the ability to walk. The device is controlled by the user’s body movements, providing real-time feedback and gradually improving motor function.
- EksoGT: The EksoGT is a wearable robotic suit designed for stroke and spinal cord injury patients. It enables users to stand, walk, and practice mobility exercises, promoting neural recovery through repetitive motion.
2. Robotic Rehabilitation Arms and Hands
In addition to exoskeletons, robotic rehabilitation arms and hands are used to help individuals with upper-limb impairments, such as those caused by stroke or brain injury, regain fine motor skills and strength. These devices assist with tasks such as reaching, grasping, and manipulating objects, all while encouraging the brain to reorganize its motor pathways.
- Armeo Spring: The Armeo Spring is a robotic arm used in therapy for stroke patients. It assists with arm movements while providing real-time feedback on the patient’s progress. The system adjusts the level of assistance based on the patient’s capabilities, helping them regain functional independence.
- Hand of Hope: The Hand of Hope is a robotic hand exoskeleton designed for stroke patients to help them recover hand function. The device provides repetitive, targeted movement assistance to retrain hand muscles and improve dexterity.
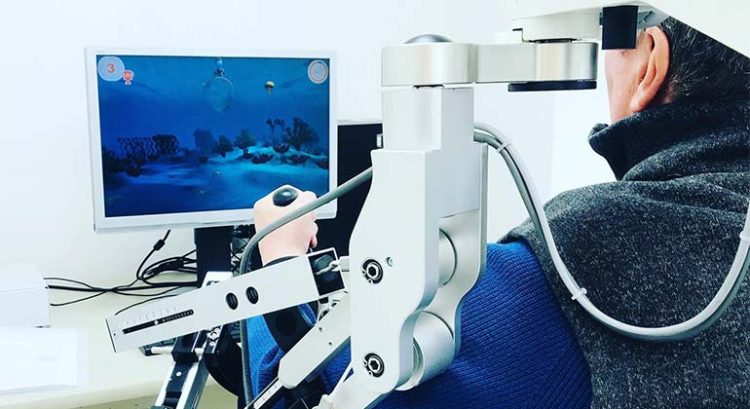
3. Virtual Reality (VR) and Robotics Integration
Virtual reality (VR) is increasingly being used in combination with robotic systems to enhance the rehabilitation experience. By immersing patients in a virtual environment, VR can provide motivational and engaging exercises while the robot assists with the physical movements.
- Interactive Rehabilitation: Virtual reality platforms like MindMaze combine VR with robotic rehabilitation to create a fully immersive therapy experience. Patients perform therapeutic exercises within a virtual world, while the robot guides their movements, offering both physical and cognitive rehabilitation.
- Gamification of Therapy: Gamified robotic therapy systems engage patients by turning rehabilitation exercises into fun, interactive games. This approach improves patient motivation, encourages consistent practice, and enhances the overall experience.
Challenges and Future Directions
1. Cost and Accessibility
Despite their promise, bionic robots remain costly, limiting their accessibility to a broader range of patients. The high expense of advanced robotic devices often puts them out of reach for many healthcare systems and patients, especially in low-resource settings.
- Affordability: To increase accessibility, it is crucial that bionic robot manufacturers focus on reducing production costs. Advances in materials and manufacturing processes may help bring prices down, making these devices more affordable for rehabilitation centers and patients.
2. Integration with Clinical Settings
While bionic robots show great promise, their integration into clinical practice remains a challenge. Healthcare professionals need training to use these devices effectively, and the devices must be optimized to work seamlessly with existing rehabilitation protocols.
- Standardization: The development of standardized protocols for the use of bionic robots in rehabilitation will be key to ensuring their effectiveness across different clinical settings. These protocols should take into account patient variability and the range of rehabilitation goals.
3. Long-Term Effectiveness
While early-stage research and trials have demonstrated the benefits of bionic robots in neurorehabilitation, further research is needed to understand their long-term effectiveness. Ongoing clinical trials and longitudinal studies will be necessary to determine how well these technologies support sustained recovery and independence in patients.
Conclusion
Bionic robots hold immense potential in the field of neurorehabilitation, offering new avenues for restoring motor function, enhancing neuroplasticity, and providing personalized, effective therapy for patients with neurological impairments. By integrating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and brain-computer interfaces, bionic robots are poised to transform the way we approach rehabilitation and recovery.
As these technologies continue to evolve, their accessibility, affordability, and integration into clinical practice will improve, making them an essential part of neurorehabilitation in the future. Through innovation, research, and continued collaboration between engineers, clinicians, and patients, bionic robots will undoubtedly play a central role in shaping the future of rehabilitation and offering new hope to individuals affected by neurological conditions.