Introduction
In the last decade, the field of robotics and material science has seen groundbreaking innovations in flexible materials and bionic muscle actuation technologies. These advancements are not only pushing the boundaries of conventional robotic systems but also creating new paradigms for soft robotics, biomimetic actuators, and human-machine interfaces. By mimicking the principles of biological muscles and incorporating soft materials into mechanical designs, these technologies have opened up a world of possibilities for creating robots and devices that are more adaptable, efficient, and capable of interacting safely with humans and delicate environments.
The importance of flexible materials in actuation cannot be overstated. While traditional robotic systems often rely on rigid structures and complex mechanical actuators, flexible materials enable the creation of more compliant, lightweight, and energy-efficient systems that mimic biological organisms. Bionic muscles—artificial actuators designed to replicate the function of biological muscles—are at the heart of this revolution, offering unprecedented advantages in terms of dexterity, strength, and flexibility.
In this article, we explore the recent advancements in flexible materials and bionic muscle actuation technologies, the mechanisms behind their operation, and the diverse applications across fields like robotics, medical devices, prosthetics, and wearable technologies. Additionally, we discuss the challenges and future directions of research in these promising areas.
The Role of Flexible Materials in Robotics and Actuation
What Are Flexible Materials?
Flexible materials are substances that exhibit high degrees of flexibility, stretchability, and deformation without breaking or losing their functional integrity. These materials are central to the design of soft robots and actuators, which aim to emulate the versatility and resilience of biological systems. Flexible materials include elastomers, polymers, composite materials, and liquid crystals, all of which can stretch, bend, or compress in response to applied forces.
Unlike traditional rigid materials used in industrial robots and machinery, flexible materials allow for the creation of soft robots—robots that are more adaptable, lightweight, and capable of safely interacting with dynamic and delicate environments.
The main characteristics that make flexible materials suitable for robotics include:
- High Stretchability: Flexible materials can extend and contract, similar to natural muscles, providing the necessary movement for soft robotics.
- Elasticity: The ability to return to their original shape after deformation enables repeated use without wear.
- Compliance: Flexible robots are less likely to damage surrounding objects or humans during interaction, which is critical for applications in medical devices and human-robot collaboration.
Why Are Flexible Materials Important for Actuation?
Traditional actuators in robotics, such as electric motors or hydraulic pistons, are rigid and require complex mechanisms for precise control. They are also limited by size, weight, and energy consumption. Flexible actuators, in contrast, provide more lightweight and efficient alternatives, offering greater dexterity and compliance.
For example, a flexible actuator can mimic the behavior of human muscle by changing its shape or stiffness in response to an external stimulus, such as an electrical current, pressure, or temperature. This allows robots to perform more dynamic tasks, from grasping objects to moving through constrained spaces, without the limitations of rigid structures.
Bionic Muscle Technology: Mimicking the Human Muscle System
Understanding Bionic Muscles
Bionic muscles are artificial actuators designed to replicate the function of biological muscles. Much like natural muscles, these bionic systems are capable of generating force, motion, and work in response to external stimuli. They are primarily designed for use in robotics, prosthetics, and medical devices, offering solutions to applications that require high flexibility, adaptability, and bio-compatibility.
In nature, muscles contract and expand through the interaction of actin and myosin filaments within the muscle fibers. To emulate this process, bionic muscles utilize various materials and mechanisms to produce motion. Some of the key techniques used to create artificial muscles include:
- Electroactive Polymers (EAPs): These are polymers that change shape or size when exposed to an electric field. They are a promising material for creating bionic muscles due to their high flexibility and large deformation capabilities. Examples include ionic polymer-metal composites (IPMCs) and dielectric elastomers.
- Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs): These materials “remember” their original shape and return to it when heated. SMAs are often used in actuators that require controlled movement, such as in robotic hands or prosthetic limbs.
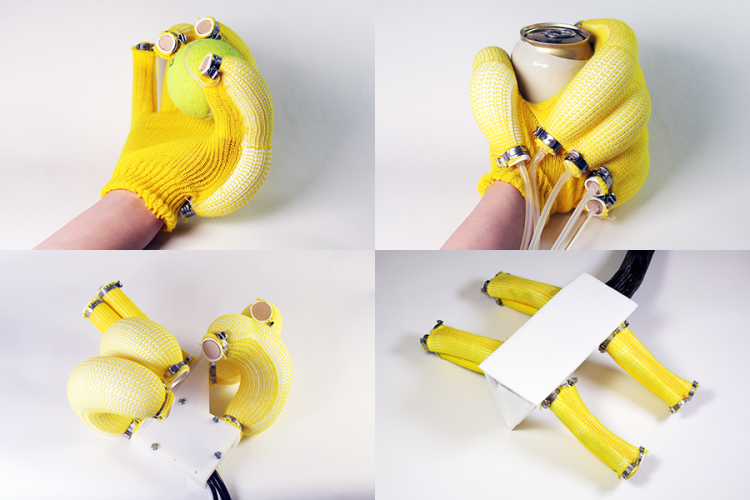
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems: Bionic muscles can also be created by using pressurized fluids or gases to inflate and deflate flexible materials. This mechanism mimics the natural expansion and contraction of muscles. Soft pneumatic actuators (SPAs) are one example of this technique.
- Artificial Muscles with Carbon Nanotubes: Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are a highly promising material for bionic muscles due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility. CNTs can be used in combination with polymers to produce actuators capable of large deformations with minimal energy consumption.
Advantages of Bionic Muscles
Bionic muscles offer numerous advantages compared to traditional mechanical actuators, including:
- High Flexibility: Bionic muscles can perform complex movements with great precision, allowing for more lifelike motion in robots and prosthetics.
- Lightweight: These muscles are typically lighter than traditional mechanical actuators, which is crucial in applications where weight is a key factor, such as wearable robotics and prosthetics.
- Scalability: Bionic muscles can be scaled for different applications, from tiny actuators in medical devices to large, powerful muscles in industrial robots.
- Energy Efficiency: Many bionic muscles, especially those based on electroactive polymers or pneumatic systems, are more energy-efficient than traditional motors or hydraulic systems, allowing for longer operation times and reduced power consumption.
Recent Advancements in Flexible Materials and Bionic Muscles
1. Electroactive Polymers (EAPs) and Their Progress
In recent years, electroactive polymers (EAPs) have made significant strides in the development of soft actuators and bionic muscles. EAPs can deform dramatically in response to an applied voltage, making them ideal candidates for artificial muscles.
Researchers have focused on improving the performance of EAPs by enhancing their actuation strain, response time, and energy efficiency. New advances in materials science, such as the use of ionic EAPs and dielectric elastomers, have led to the creation of highly flexible, fast-response actuators with greater durability.
- Ionic Polymer-Metal Composites (IPMCs): These EAPs are highly flexible and can generate large displacements when an electric field is applied. IPMC-based artificial muscles have been developed for applications in soft robotics and prosthetics.
- Dielectric Elastomers: These are EAPs that change shape in response to an electric field. Due to their high actuation strain and energy efficiency, dielectric elastomers have been utilized in soft actuators for robotics, including muscle-like actuators capable of performing delicate tasks.
2. Advancements in Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs)
Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) are another material that has seen significant development in recent years. These materials are capable of returning to their original shape when exposed to heat, making them ideal for applications that require precise, controlled motion.
Recent improvements in SMA technology have focused on increasing the material’s response speed, fatigue resistance, and temperature stability. Researchers have also developed hybrid systems combining SMAs with other materials like elastomers or composites to improve performance and reliability.
- Actuators for Prosthetics: SMA-based actuators have been used in the development of prosthetic hands and fingers, offering fine motor control and dexterity.
- Robotics and Aerospace: SMAs have been explored for use in space exploration, where their lightweight and responsive nature is an advantage in microgravity environments.
3. Soft Pneumatic Actuators (SPAs)
Soft pneumatic actuators (SPAs), which use air pressure to create motion, have gained popularity due to their simplicity and flexibility. These actuators are capable of producing smooth, continuous motion, making them ideal for applications requiring soft, compliant interaction with objects or humans.
Recent developments in SPA technology have focused on improving control systems to allow for more precise and adaptive movements. This has led to the creation of soft robots that can perform delicate tasks such as gripping fragile objects or human-robot collaboration in shared workspaces.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): SPAs have been integrated into cobots that work alongside human operators in industries like assembly, manufacturing, and healthcare. These robots can adapt their movement and force to interact safely with humans.
4. Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) in Bionic Muscle Development
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are being incorporated into the development of artificial muscles due to their remarkable properties, including strength, flexibility, and conductivity. When combined with polymers or elastomers, CNTs can produce highly efficient actuators capable of significant deformation under low electrical voltage.
Recent studies have demonstrated that CNT-based actuators can achieve large-scale deformations, making them suitable for applications requiring both strength and flexibility, such as robotic arms, prosthetic limbs, and wearable exoskeletons.
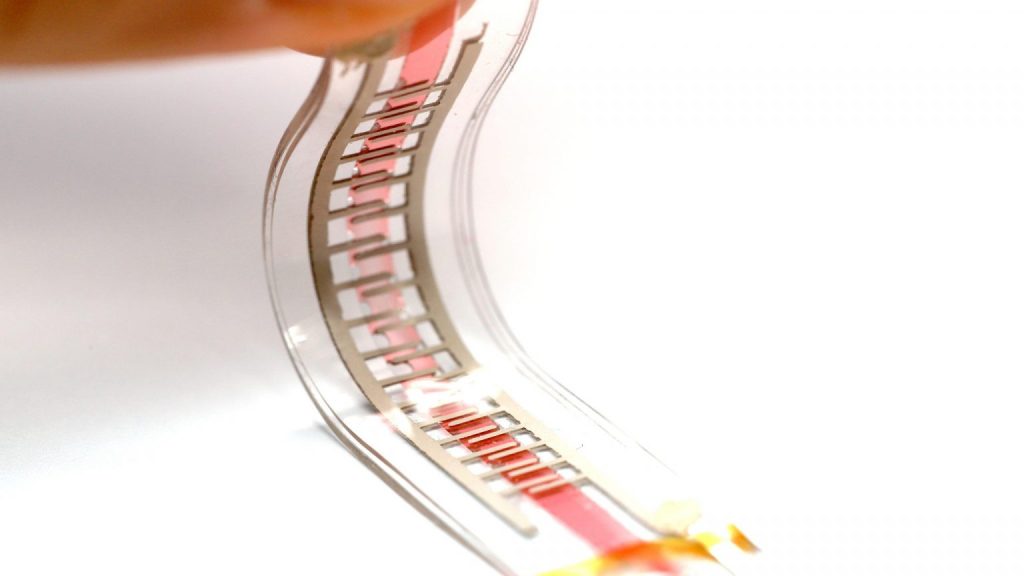

Applications of Flexible Materials and Bionic Muscles
1. Soft Robotics
Soft robots, which use flexible materials and bionic muscle actuators, have the potential to revolutionize industries that require robots to operate in complex, dynamic environments. Unlike traditional rigid robots, soft robots can adapt to their surroundings, handle delicate objects, and move with fluid, human-like motions. Applications include:
- Healthcare and Surgery: Soft robots are used for minimally invasive surgery, where their flexibility allows them to navigate tight spaces and interact with delicate tissues.
- Agriculture: Soft robots equipped with flexible actuators can handle delicate crops, such as fruit picking, without damaging them.
2. Prosthetics and Exoskeletons
Bionic muscles and flexible materials are also playing a key role in the development of prosthetic limbs and exoskeletons. These technologies enable prosthetics that mimic the natural movement of human limbs, providing a better quality of life for amputees and individuals with mobility impairments. Exoskeletons with flexible actuators are also being developed to assist with rehabilitation and enhance human strength for industrial or military applications.
3. Wearable Robotics
Wearable robotic devices, such as exoskeletons and assistive devices, are increasingly using flexible actuators to improve comfort and mobility. These devices help wearers perform daily tasks and reduce strain on muscles and joints. Key applications include:
- Rehabilitation Devices: Soft, flexible actuators are used in wearable rehabilitation systems to support recovery after injury or surgery.
- Exoskeletons for Mobility: Flexible actuators help exoskeletons assist individuals with paralysis or mobility impairments in walking, standing, or lifting.
Conclusion
Recent advances in flexible materials and bionic muscle actuation technologies are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in robotics, prosthetics, and wearable technologies. By mimicking the flexibility and efficiency of biological muscles, these technologies are enabling the development of more adaptable, efficient, and safe systems. While challenges remain, particularly in terms of material longevity, scalability, and energy consumption, the future of flexible actuators and bionic muscles holds immense promise for applications in healthcare, robotics, and human-robot interaction.
As these technologies continue to evolve, we are likely to see even more sophisticated and capable systems emerge, further blurring the lines between machines and living organisms.