Introduction
The advent of robotics in healthcare has transformed the landscape of modern surgery. Among the most prominent examples of this transformation is the Da Vinci Surgical System, a robotic platform that has significantly impacted the way surgeries are performed worldwide. Developed by Intuitive Surgical, the Da Vinci system allows surgeons to perform highly complex procedures with greater precision, flexibility, and control than ever before. This technology has not only improved patient outcomes but has also set new standards in minimally invasive surgery.
In this article, we will explore the development, capabilities, and applications of the Da Vinci Surgical Robot, its impact on the healthcare industry, the benefits and challenges associated with its use, and the future of robotic-assisted surgeries. By examining how this groundbreaking technology works, the potential it holds, and its implications for healthcare, we can gain a deeper understanding of the profound changes happening in modern surgery.
1. The Evolution of Robotic Surgery
1.1 The Genesis of Robotic Surgery
The idea of using robots in surgery dates back several decades. Initially, robotic surgery was envisioned as a way to overcome the limitations of human dexterity, control, and precision. The development of the Da Vinci Surgical Robot marks a significant leap forward in the evolution of robotic surgery, offering capabilities that were once thought to be impossible.
1.2 Early Beginnings: The Role of Computers in Surgery
In the early stages, robotic systems were largely driven by computer-assisted surgery (CAS) technologies. These systems allowed surgeons to visualize and navigate the human body with greater accuracy using computer-generated images. However, these systems were limited in their ability to perform actual surgical tasks. The next step was to create systems that could replicate or even surpass human capabilities in terms of precision and dexterity.
1.3 The Introduction of the Da Vinci Surgical System
Launched in the early 2000s, the Da Vinci Surgical System was designed to bridge the gap between human expertise and machine precision. The system was named after the renowned Renaissance polymath Leonardo da Vinci, who conceptualized the first human-powered robot centuries earlier. The Da Vinci robot represented a breakthrough, offering surgeons enhanced visualizations, robotic arms with unparalleled dexterity, and a higher level of control during surgeries.
2. How the Da Vinci Surgical System Works
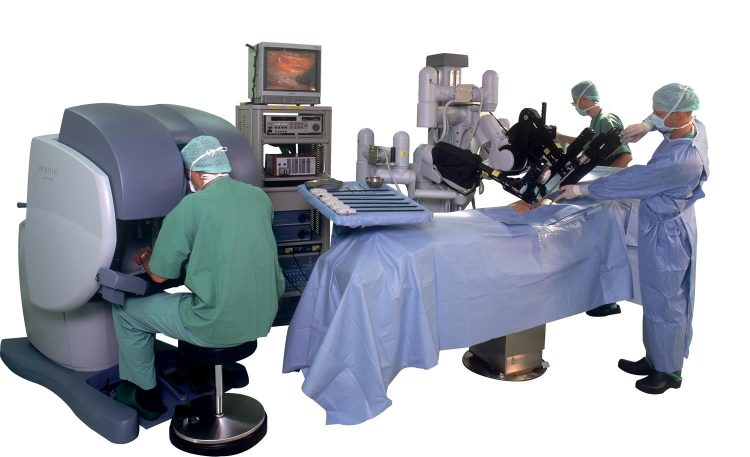
2.1 The Components of the Da Vinci System
The Da Vinci Surgical Robot consists of several key components that work in tandem to provide surgeons with enhanced precision and control:
- Surgeon’s Console: The surgeon operates the robot from a console that offers a 3D high-definition view of the surgical area. This allows for enhanced depth perception and better visualization of critical tissues and organs.
- Patient-side Cart: This is the robotic arm system that is positioned next to the patient. It consists of multiple arms, each equipped with specialized instruments that can perform a variety of surgical functions, from cutting and suturing to cauterizing tissue.
- EndoWrist Instruments: These instruments are attached to the robotic arms and are designed to mimic the natural movements of the surgeon’s hands with incredible precision. They can rotate and move in ways that are impossible for human hands, allowing for more precise cuts and sutures.
2.2 The Role of Robotics in Minimally Invasive Surgery
The Da Vinci Surgical System is primarily used for minimally invasive surgeries, which involve making smaller incisions in the body compared to traditional open surgeries. Minimally invasive techniques reduce recovery time, minimize pain, and lower the risk of infection for patients. Robotic systems, like the Da Vinci, enhance these procedures by allowing surgeons to perform delicate movements with greater accuracy.
The key benefits of minimally invasive surgery with robotic assistance include:
- Smaller incisions
- Reduced blood loss
- Faster recovery times
- Decreased postoperative pain
- Shorter hospital stays
2.3 The Surgeon’s Role and Control
One of the unique features of the Da Vinci Surgical Robot is that the surgeon remains in full control during the procedure. The robotic arms are not autonomous; rather, they act as an extension of the surgeon’s hands. The surgeon’s movements are transmitted through a series of sophisticated sensors, allowing them to manipulate the robotic arms with high precision.
This capability provides greater stability and control during surgery, especially in challenging areas such as the prostate or heart. The precision of the Da Vinci system enables surgeons to perform tasks that require exceptional dexterity, such as delicate tissue dissection or suturing.

3. Applications of the Da Vinci Surgical Robot
3.1 General Surgery
The Da Vinci Surgical Robot is used across a wide range of general surgical procedures. It has become particularly useful in surgeries such as:
- Gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy)
- Hernia repair
- Colorectal surgery
- Bariatric surgery (weight loss surgeries)
The robot’s ability to perform precise and controlled movements makes it ideal for complex procedures where traditional methods might be too invasive or difficult to execute.
3.2 Urological Surgery
One of the most common uses of the Da Vinci Surgical System is in urological surgeries, particularly prostatectomies for prostate cancer treatment. The robot’s precision allows surgeons to remove cancerous tissue while preserving surrounding healthy tissues, such as nerves, that are crucial for preserving erectile function and continence.
Additionally, the Da Vinci robot is used for:
- Kidney surgery
- Bladder cancer surgery
- Renal transplantation
3.3 Gynecological Surgery
The Da Vinci Surgical Robot has revolutionized gynecological surgery, enabling minimally invasive procedures for conditions like uterine fibroids, endometriosis, and ovarian cancer. Surgeries such as hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) can now be performed with smaller incisions, leading to shorter recovery times and reduced complications.
3.4 Cardiothoracic Surgery
In cardiothoracic surgery, where precision is critical, the Da Vinci Surgical System is increasingly used for complex procedures such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), heart valve repairs, and lung surgeries. The robot’s ability to work within the small, constrained space of the chest cavity allows for less invasive approaches and improved outcomes.
3.5 Other Specialty Areas
The Da Vinci Surgical Robot is also being used in several other medical specialties, including ear, nose, and throat (ENT) surgery, spinal surgery, and neurological surgery. Its versatility makes it suitable for various applications in both adult and pediatric populations.
4. Benefits and Limitations of the Da Vinci Surgical System
4.1 Key Benefits
- Enhanced Precision: The robotic arms allow for more precise movements than the human hand, reducing the likelihood of errors in delicate surgeries.
- Better Visualization: Surgeons can view the surgical area in 3D with high-definition imagery, enhancing their ability to navigate and perform intricate tasks.
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions mean less trauma to the body, leading to quicker recovery, reduced pain, and fewer complications.
- Shorter Hospital Stays: Due to quicker recovery times, patients can often leave the hospital sooner, which lowers overall healthcare costs.
4.2 Limitations
- Cost: The Da Vinci Surgical System is an expensive piece of equipment, with costs running into the millions of dollars for both purchase and maintenance. This can make it inaccessible for some hospitals, particularly in lower-resource settings.
- Training Requirements: Surgeons must undergo extensive training to operate the robotic system effectively, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Limited Tactile Feedback: While the robot offers enhanced visualization, it lacks the tactile feedback that a surgeon would experience with their own hands. This can make certain aspects of surgery, such as tissue palpation, more difficult.
5. The Future of Robotic Surgery
5.1 Technological Advancements
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect significant improvements in robotic surgery. These advancements include:
- Improved AI Integration: Artificial intelligence will play an increasingly important role in robotic surgery, providing enhanced decision support, real-time analysis, and predictive analytics to assist surgeons.
- Miniaturization: As robotic systems become more compact, they will become more versatile and applicable to a wider range of medical procedures, including those that require even smaller incisions.
- Autonomous Systems: While current systems require a human operator, future robotic platforms may incorporate greater levels of autonomy, allowing robots to perform certain procedures independently or with minimal guidance.
5.2 Expanded Applications
With ongoing research and development, the use of robotic surgery is expected to expand into more areas of medicine, from regenerative surgery to personalized medicine. As robotic systems become more sophisticated, they will be able to perform an even greater range of surgeries with enhanced precision.
5.3 Global Adoption and Accessibility
One of the future goals for robotic surgery is to make these systems more accessible globally. This involves reducing costs, simplifying training, and ensuring that robotic platforms can be used in various healthcare settings worldwide.
Conclusion
The Da Vinci Surgical Robot has significantly transformed the landscape of modern surgery by providing enhanced precision, flexibility, and control during operations. It has proven particularly valuable in minimally invasive surgery, offering benefits such as reduced recovery times, fewer complications, and improved patient outcomes.
While there are still challenges to overcome, particularly in terms of cost and accessibility, the future of robotic surgery looks bright. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of robotic systems like the Da Vinci platform will continue to expand, opening new possibilities in healthcare and revolutionizing the way we approach surgery.