1. Introduction: The Aging Population and the Need for Elderly Care
The global population is aging at an unprecedented rate, creating a pressing need for innovative solutions in elderly care. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of people aged 60 years and older will increase from 1 billion in 2020 to 1.4 billion by 2030. This demographic shift places considerable strain on healthcare systems, family caregivers, and social services worldwide.
With traditional caregiving systems already facing resource shortages and an increasing burden on healthcare workers, robotics technology has emerged as a powerful tool to help address these challenges. Robots equipped with advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, and sensors are being developed to assist with a variety of tasks, including physical support, monitoring health, providing companionship, and improving overall well-being.
This article examines how robotic technology can enhance elderly care, exploring its current applications, benefits, challenges, and future possibilities in transforming healthcare for the elderly.
2. The Role of Robotics in Elderly Care
2.1 Types of Robots Used in Elderly Care
Various types of robots have been developed to address the unique needs of elderly patients. These robots can be broadly categorized into assistive robots, companion robots, and healthcare robots, each of which plays a vital role in improving elderly care.
2.1.1 Assistive Robots
Assistive robots are designed to provide physical support for elderly individuals, especially those with mobility impairments. These robots can help with tasks such as:
- Transferring patients from bed to wheelchair or vice versa
- Supporting walking and maintaining balance
- Helping with daily activities, like dressing, eating, and grooming
Robots like Honda’s ASIMO and Robear, developed by Japan’s RIKEN Institute, are examples of assistive robots that can lift and move patients with limited mobility, offering a significant improvement in the quality of life for elderly individuals.
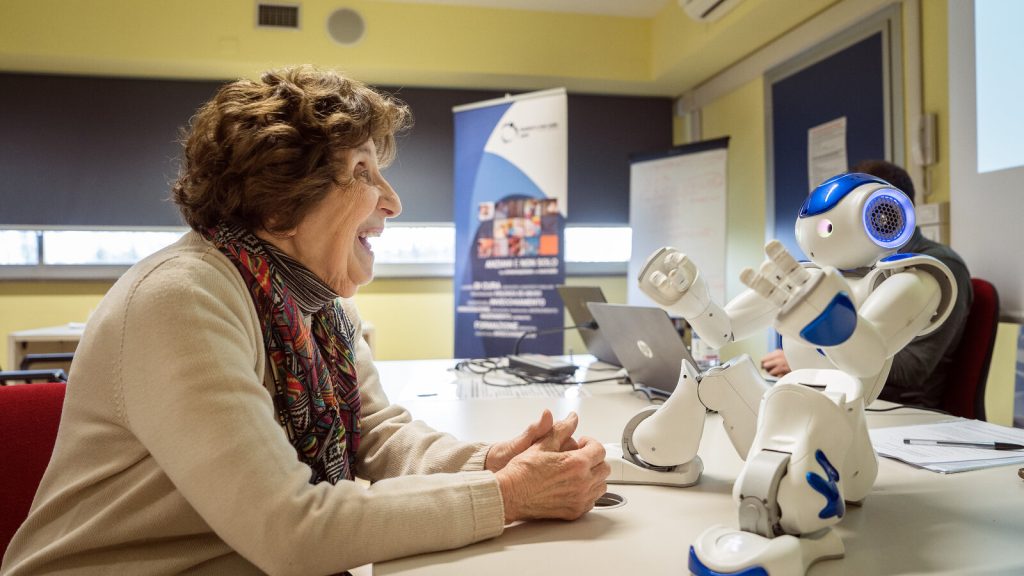
2.1.2 Companion Robots
Companion robots provide social interaction and emotional support for elderly patients, helping to combat loneliness and depression. These robots are equipped with natural language processing (NLP) capabilities and can engage in conversation, play games, and even offer reminders for medication or appointments. Popular examples include:
- Pepper by Softbank Robotics, which can interact with patients and offer emotional companionship.
- Jibo, designed to serve as a friendly companion, helping the elderly feel less isolated.
The psychological benefits of companionship robots are particularly significant for elderly patients in nursing homes or those living alone.
2.1.3 Healthcare Robots
Healthcare robots assist in monitoring and managing the health of elderly patients. These robots can:
- Monitor vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen levels
- Administer medications and track their usage
- Alert healthcare professionals if a patient’s health deteriorates
Telepresence robots, which allow doctors to remotely diagnose and interact with patients, are another critical innovation. For example, Telenoid and VGo enable remote consultations, making it easier for elderly patients to receive medical attention without leaving their homes.
2.2 Benefits of Robotic Technology in Elderly Care
2.2.1 Improving Physical Health and Independence
One of the most significant benefits of robotics in elderly care is that it enhances physical health by offering support with mobility and daily activities. Robotic systems like assistive exoskeletons and mobility aids help elderly patients perform basic tasks that might otherwise be challenging, promoting greater independence. These systems are particularly helpful for elderly individuals with muscle weakness, arthritis, or neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease.
2.2.2 Reducing Caregiver Burden
Family members and healthcare professionals are often overwhelmed by the physical and emotional demands of caregiving. Robots can reduce this burden by assisting with tasks such as lifting patients, helping them move around, and reminding them to take medications. This alleviates the physical strain on caregivers and enables them to focus on more specialized care.
2.2.3 Enhancing Mental Health and Well-being
Loneliness and isolation are common among elderly individuals, particularly those living alone or in long-term care facilities. Companion robots can provide emotional support and companionship, which has been shown to reduce feelings of loneliness and improve mental health. Regular social interactions with robots can help elderly patients feel more engaged, improving their overall well-being.
2.2.4 Increasing Efficiency in Healthcare Delivery
Robots can also increase the efficiency of healthcare delivery by automating routine tasks, monitoring patients’ health remotely, and providing real-time data to healthcare providers. For example, robots can alert doctors or family members if a patient falls or experiences a health emergency. This early detection can lead to quicker interventions and better health outcomes.

3. Challenges and Limitations of Robot-Assisted Elderly Care
3.1 Technological Limitations
While the potential for robotic technology in elderly care is significant, there are still several technological challenges to overcome. For instance, robots may struggle with performing tasks in unstructured environments or interacting with patients in ways that are intuitive for humans. Advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic dexterity are necessary to ensure that robots can function effectively in a variety of caregiving contexts.
3.2 Ethical and Social Concerns
As robots play an increasingly prominent role in elderly care, ethical questions arise regarding patient autonomy, privacy, and the role of human caregivers. Some patients may feel uncomfortable or distrustful of robotic systems, and the potential for robots to replace human caregivers could lead to job losses in the healthcare industry. Furthermore, the integration of robots into elderly care must address concerns regarding data privacy and security, particularly when dealing with sensitive health information.
3.3 Cost and Accessibility
The high cost of advanced robots and AI systems remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption in elderly care. Although the cost of robotic technology has decreased in recent years, many families and care facilities may find it difficult to justify the investment. Furthermore, ensuring that robotic systems are accessible to elderly individuals with varying levels of physical and cognitive abilities requires careful design and user-friendly interfaces.
4. Future Directions for Robotic Technology in Elderly Care
4.1 Advancements in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
The future of robotic technology in elderly care lies in further advancements in AI and machine learning. Future robots will be more capable of understanding and adapting to the needs of elderly patients. For instance, robots may be able to provide personalized care by learning from patient behavior, health data, and feedback. AI could also enable robots to detect early signs of conditions like Alzheimer’s or dementia, allowing for earlier interventions.
4.2 Integration with Smart Homes
The integration of robots with smart home technology will allow elderly individuals to live more independently. For example, robots could communicate with smart devices like voice assistants, thermostats, and lighting systems, enabling elderly patients to control their environment more easily. Combined with home sensors, robots could assist with daily tasks such as cooking, cleaning, and monitoring environmental factors like air quality or temperature.
4.3 Collaborative Care Models
In the future, robots will work in collaboration with human caregivers to provide more comprehensive and effective care. This hybrid approach combines the strengths of both human and robotic systems, with robots performing tasks that require high precision and routine care, while human caregivers focus on complex emotional and medical needs. This model will likely be crucial in long-term care facilities, where the human workforce is often stretched thin.
5. Conclusion
The potential for robotic technology to transform elderly care is vast. As the aging population grows, robots will play an increasingly important role in supporting the elderly, improving their quality of life, and relieving the burden on caregivers. From assistive robots that aid in mobility to companion robots that offer emotional support, technology offers innovative solutions to the challenges of elderly care.
Despite the challenges—such as technological limitations, ethical concerns, and cost—robotic technology is steadily advancing and will continue to evolve. By integrating AI, machine learning, and smart home systems, future robots will provide even more personalized, adaptable, and efficient care for elderly patients.
Ultimately, robots are not meant to replace human caregivers but to complement them, enabling a more sustainable and humane approach to elderly care. As we move forward, the collaboration between robotics, healthcare professionals, and families will be key to ensuring that elderly individuals receive the care, dignity, and support they deserve.